Let’s say you’re browsing an online store late at night, checking out a cool new pair of shoes. You leave without buying. The next day, you see an ad for those exact shoes on a news site. Later, you even get an email from the store saying, “Hey, your cart is waiting!” That’s the magic of Retargeting vs Remarketing at work.
In simple words, retargeting is when ads follow people online after visiting your website, and remarketing is when you reconnect with people through email or messages after they’ve already interacted with you.
Curious to know how this works and when to use each one? Keep reading. We’re breaking it all down in detail with examples, tips, and real-life cases.
What is Retargeting?

Let’s say someone visits your website and looks at a product but doesn’t buy it. Later, they visit another website (like a news site or social media), and they see an ad from your website reminding them of that product. That’s retargeting.
Retargeting is all about showing online ads to people who have interacted with your website or app, like clicking on a product or adding it to the cart, but haven’t bought anything yet.
It works by tracking users with cookies or tracking pixels. As users browse the internet, your ads follow them around to remind them about your product or service.
What is Remarketing?

Now, imagine someone has already bought something from your website, or they signed up for your emails. A few weeks later, you send them a message like:
- “You haven’t visited us in a while – here’s a 10% discount!”
- “Your subscription is ending – renew now and get a free bonus.”
That’s remarketing.
Remarketing is about reaching people who have already given you their contact details, like email, phone number, or account login. You talk to them using emails, SMS messages, or even push notifications.
Retargeting vs Remarketing: Quick Comparison Table
Here’s the difference between remarketing and retargeting presented in a table.
| Feature | Retargeting | Remarketing |
| Audience | Website visitors who didn’t convert | Customers who already gave contact info |
| Channel | Display ads, social media ads | Email, SMS, push notifications |
| Main Goal | Convert potential new customers | Re-engage existing customers |
| Uses Cookies? | Yes | Not always |
| Example | Ads follow you after viewing shoes | Email reminds you to renew subscription |
Real-Life Examples of Retargeting and Remarketing
Let’s look at how big brands use both strategies:
| Company | Strategy Used | Example |
| Amazon | Retargeting | Shows ads of products you looked at but didn’t buy |
| Netflix | Remarketing | Sends emails when new content is available or when you’re inactive |
| Spotify | Both | Ads to free users (retargeting) + Emails for upselling premium (remarketing) |
| PetSmart | Remarketing | Offers loyalty rewards via email or SMS |
| Nike | Retargeting | Shows dynamic ads based on what you viewed on their site |
How Do Retargeting and Remarketing Work?
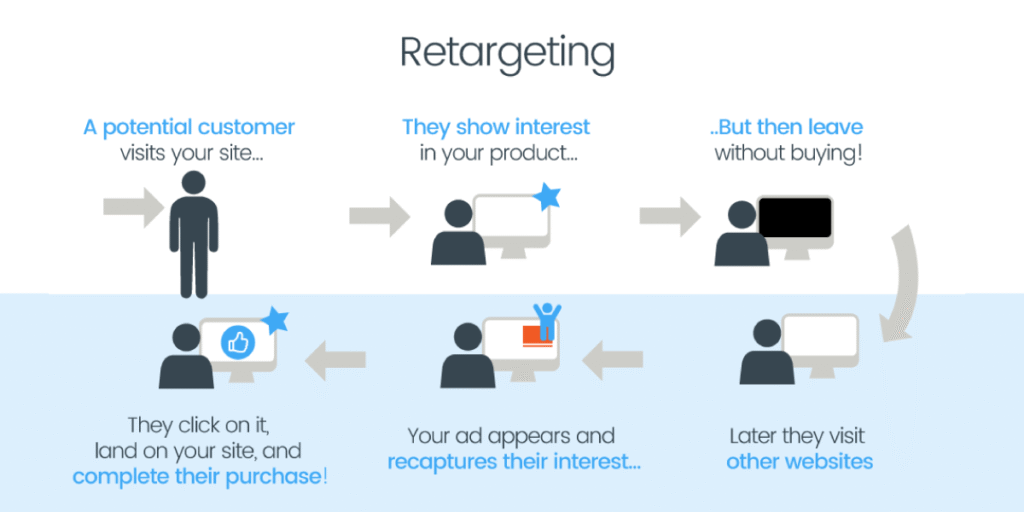
Here’s how both work in detail, explained.
Retargeting Step-by-Step:
- Someone visits your website.
- A cookie or tracking code is added to their browser.
- They leave your site without buying.
- You show them ads on other websites they visit.
- If done right, they come back and buy.
Remarketing Step-by-Step:
- Someone buys from you or signs up (gives email or phone).
- You store their info.
- You send emails, texts, or push notifications.
- You remind them about offers, new products, or renewals.
- They come back to buy again or stay subscribed.
What Kind of Data is Used?: Remarketing vs Retargeting
When it comes to the kind of data these two strategies use, retargeting usually works with cookies, browsing behavior, and what products people looked at on your site. It’s all about tracking what they do without needing their personal info.
On the other hand, remarketing uses details that people have already given you, like their email address, phone number, what they bought before, or their account details. But here’s something important you should know.
Google is phasing out third-party cookies, so retargeting is now moving toward newer methods like using first-party data collected directly from your site or tools like the Conversion API.
Why Should You Care About This?
Because most people don’t buy on the first visit. Studies say:
- Around 97% of visitors leave a website without buying anything.
- Retargeted ads have 10x higher click-through rates than regular ads.
- Remarketing emails have open rates around 45%, which is much higher than cold emails.
So if you’re not using retargeting or remarketing, you’re losing potential customers.
When Should You Use Retargeting?
Use retargeting if:
- You want new customers.
- You run brand awareness ads and need to convert visitors.
- You sell one-time products (like furniture, electronics).
- Your product is high-cost, and customers need time before buying.
Example: A customer sees a sofa on your website but doesn’t buy it. You show them ads for that sofa on other websites, hoping they return and buy.
When Should You Use Remarketing?
Use remarketing if:
- You want repeat purchases.
- You sell subscriptions or consumables (coffee, vitamins, etc.).
- You want to upsell or cross-sell.
- Your marketing budget is small (emails are often free or cheap).
Example: A customer hasn’t ordered coffee in 3 weeks. You send them an email with “10% off your next order” to bring them back.
For more easy strategies, you might like Facebook Marketing for Small Businesses in 2025, which shows how to reach more people on a small budget.
The Blurry Line Between the Two
These days, the line between retargeting and remarketing is getting blurry. For example, you can take your email list—people who already gave you their contact info—and upload it to Facebook or Google.
Then, you can show those same people paid ads. Now, even though it’s your email list (which sounds like remarketing), you’re using ad platforms (which feels like retargeting). So, it’s kind of a mix of both.
That’s why, instead of stressing over the name, what really matters is your strategy—how you plan to reach people and get them to come back.
| If you find this topic of retargeting and remarketing helpful and want to learn how to use these strategies for your own business, there are many great e-learning courses on Mastery Bay you should check out. It covers marketing & promotion in a simple, practical way. Perfect for beginners or anyone wanting better results. Mastery Bay offers step-by-step e-learning so you can easily turn what you’ve read here into real success. |
Best Practice Tips
For Retargeting:
- Use frequency caps (don’t annoy users with too many ads).
- Segment your audience by behavior.
- Try dynamic ads that adjust based on user behavior.
For Remarketing:
- Personalize emails based on previous purchases.
- Use automation tools to send emails or texts.
- Always offer value (discounts, news, new arrivals).
Wrapping Up: Which One Should You Use Between Retargeting vs Remarketing?
Honestly, you should use both.
It’s not retargeting or remarketing. It’s retargeting AND remarketing.
Here’s a quick final thought chart:
| If You Want To… | Use This |
| Get back visitors who didn’t buy | Retargeting |
| Remind customers to buy again | Remarketing |
| Show ads across the web | Retargeting |
| Send personalized emails or SMS | Remarketing |
| Upsell or cross-sell | Remarketing |
| Get new customers to convert | Retargeting |
Basically, they both work towards the same goal: more sales, better engagement, higher lifetime value. Use them together to build smarter, more effective marketing campaigns.
Also, if you’re looking for practical ways to grow your business, check out 8 steps on how to use Facebook groups for marketing for simple tips.
FAQs
- What is the main purpose of retargeting in marketing?
The main goal of retargeting is to bring back people who visited your site but didn’t buy anything. It reminds them through ads while they browse other sites. - Can I use retargeting if I don’t have a big budget?
Yes, you can start small with retargeting ads on platforms like Google or Facebook. It’s often more cost-effective because you’re targeting people already interested.
- Is remarketing only done through emails?
No, remarketing can also include text messages, app notifications, or even targeted ads to existing customers. The key is using customer info you already have.
- How long should I run a retargeting campaign?
Most businesses run retargeting campaigns for a few weeks to a month. It depends on your goals, but it’s good to keep testing and adjusting.
- Do I need special tools to start remarketing?
Not really, just an email list and a tool like Mailchimp or Klaviyo can help. These tools let you send messages to customers who already know your brand.
- Is it okay to use both retargeting and remarketing together?
Absolutely yes. Using both helps you reach more people—some who are just browsing and others who already bought from you before.
- Can retargeting annoy my website visitors?
It can, if you show them too many ads too often. That’s why it’s smart to set limits on how many times people see your ads each day.
- What kind of businesses should use remarketing?
Any business with returning customers or subscriptions should use remarketing. It helps you stay connected and bring people back to buy again.
- How do I measure if my retargeting is working?
You can track clicks, website visits, and sales through your ad platform dashboard. If people are coming back and buying, it’s working well.
- What happens to retargeting with no more third-party cookies?
Retargeting will rely more on first-party data and tools like conversion APIs. It just means you need to collect data directly from your own website now.